Solar power is defined as “use of the sun’s energy either directly as thermal energy (heat) or through the use of photovoltaic cells in solar panels and transparent photovoltaic glass to generate electricity.” Across the world, solar energy is playing an important transition role from dependence on traditional forms of energy such as coal to renewable energy.
The total global solar PV installed capacity had increased more than 400 GW by the end of 2017. The major countries which contributed to this growth factor are China, USA, Japan and India. Nanotechnology is another promising area which will help to improve the solar power in the coming years. There are multiple applications under development in nanotechnology which will improve solar cells.
The government of India is aggressive in popularizing solar power. The country has reportedly clocked more than 50% annual growth in solar power installation since 2016. Major trends associated with solar energy are listed below;
- The solar module prices have reduced by 29% to US$32 cents/WP in 2017. This reduction of price has resulted in strong demand for Photovoltaic system in emerging economies.
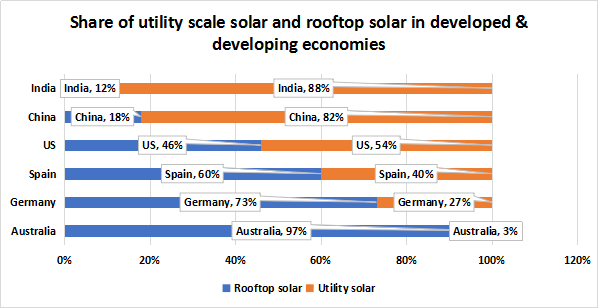
- Governments in emerging economies have focused their intentions on rooftop solar growth, while developed countries are focusing on utility-scale solar projects as illustrated below.
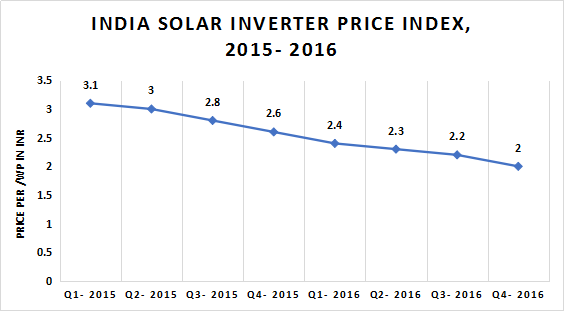
The Indian Solar Inverter Price Index has reduced from INR 3.1/WP in the first half of 2015 to INR 2.0/WP by the end of 2016 due to increase in supply slide surplus.
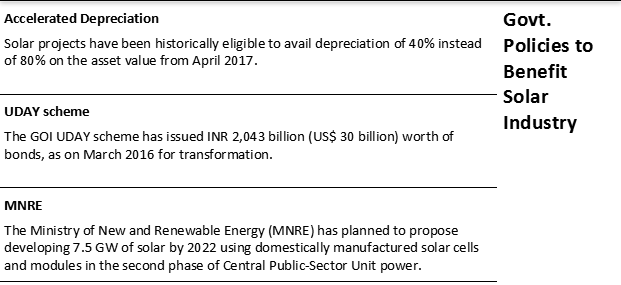
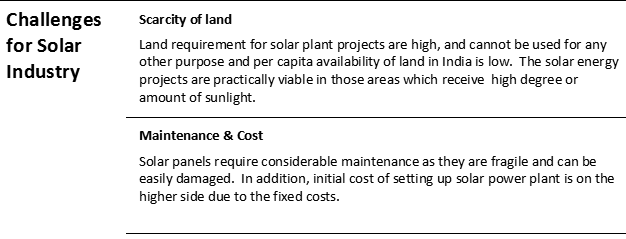
The initiatives of India government to drive growth in solar demand as well as associated challenges in achieving those goals are summarized below;