The Banking Sector in India has undergone a paradigm shift from traditional banking to digital banking over the past decades.
In spite of the global economic turn down, the India’s Banks are sufficiently capitalized to resilient the macro-economic risks. Today there are 19 Public sectors banks are there in India including State Bank of India. In addition to that there are 49 foreign banks, 56 regional rural banks, 1,562 urban cooperative banks and 94,384 rural cooperative banks operating in India.
Indian Banks are increasing focus on adopting an integrated approach to risk management. Banks have already accepted the international banking supervision accord of Basel II and majority of banks have already met the capital requirement of Basel III.
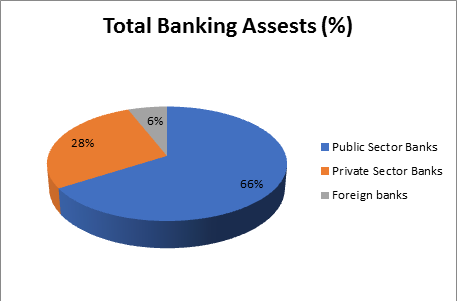
From 2013-2018, the total banking sector asset (Public, Private and Foreign Banks) The public sector banks contributes $1,557.04 (66%) and public sector and private banking contributes around $666.99 (28%). The remaining $135.96 (6%) contributed by foreign banks.
In the 2018 Private bank interest income reached $47.39 billion, whereas public sector bank interest income stood at $102.46 billion.
The credit market in India is the fourth largest market worldwide. It increased to $281 billion in 2017 from $181 billion on 2014. The total lending has also increased at a CAGR of 11% during the financial year 2007-2018 and the deposits increased by 11.66% CAGR during the same period.
Increase in number of internet users is proving a boost to the digital banking along with that the policy formed by the government like Banking regulation bill, Insolvency and bankruptcy code ordinance will help the banks to fight against the NPA and will strength the overall banking sector